Introduction
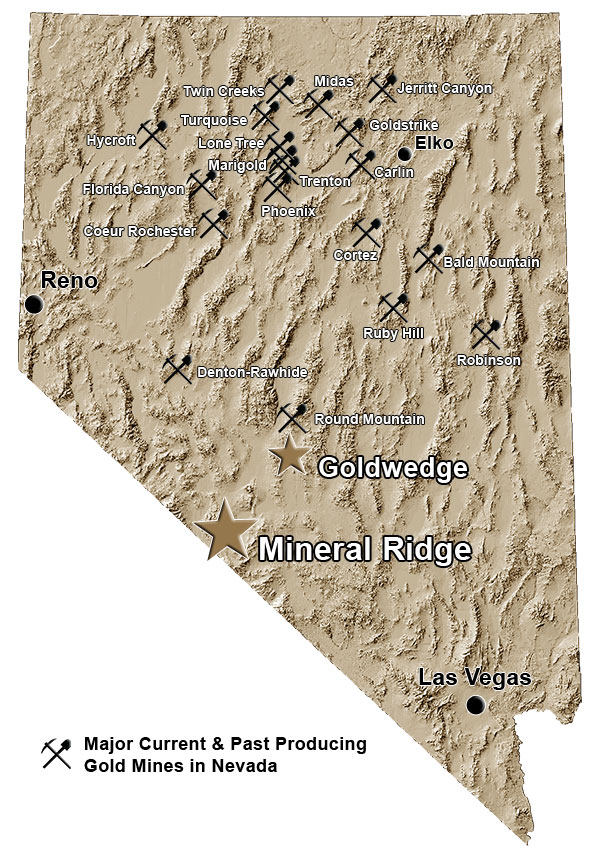
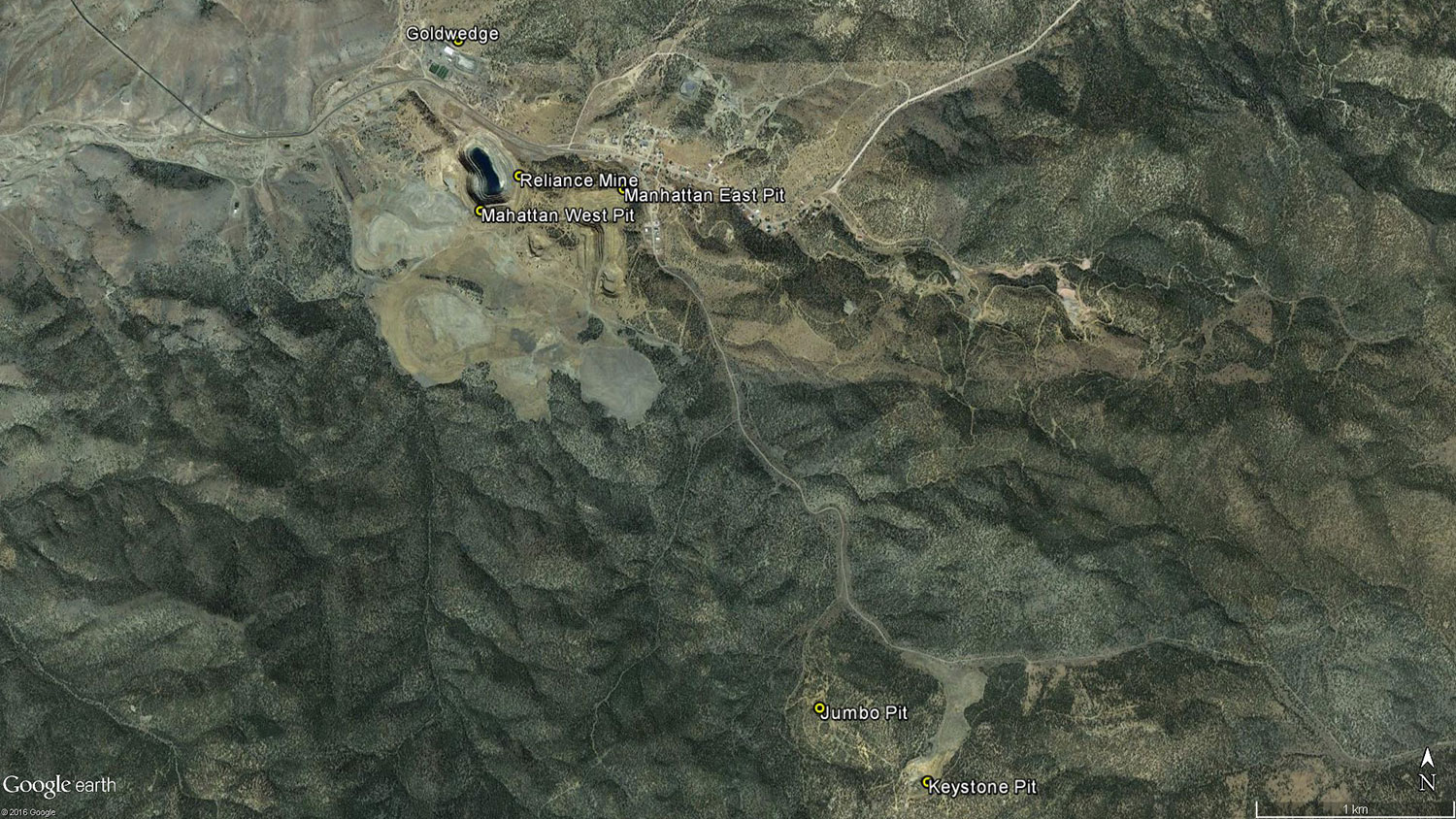
The 100% owned Goldwedge property is located 54 km north-northeast of the town of Tonopah within the Manhattan Mining District of south-central Nevada. The 726 hectare (1,795 acre) property covers three separate claim blocks and encompasses the Goldwedge, Keystone and Jumbo gold deposits.
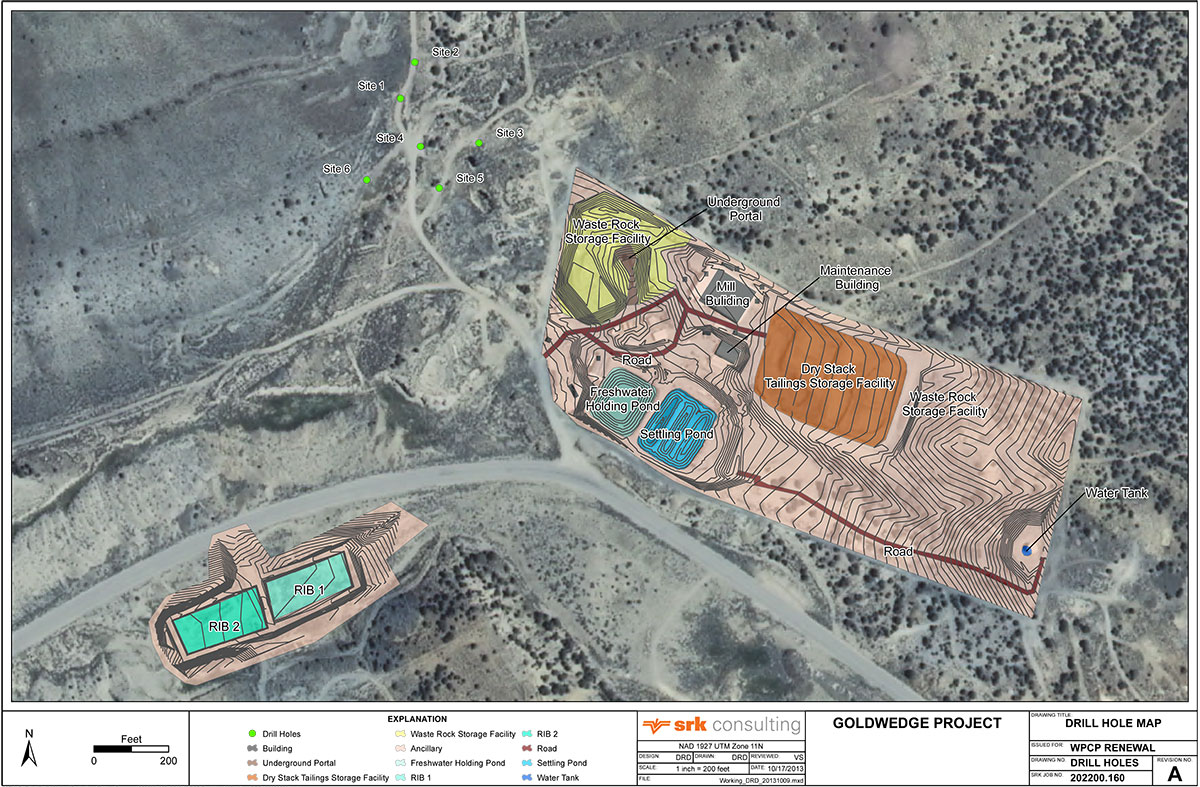
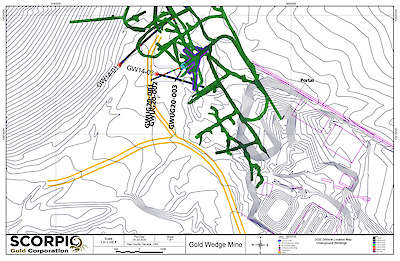
The northern claim block encompassing the Goldwedge deposit includes a fully permitted underground mine with over 600 m of development and a 400 tpd mill facility with gravity circuit.
Goldwedge Deposit
Goldwedge Deposit
The Goldwedge deposit lies within the Walker Lane Gold Belt and is situated on the southern periphery of the Manhattan Caldera, approximately 16 kilometers south of the 15 million ounce Round Mountain Mine. Historic mining in the Manhattan Mining District dates back to the 19th century, with district-wide gold production from both lode and placer deposits estimated at 566,000 ounces. The largest gold production came from the Manhattan Mine East & West pits located within a kilometer south of the Goldwedge deposit, where Echo Bay Mines reportedly produced an estimated 236,000 ounces.
A number of companies have explored the underground potential of the Goldwedge deposit, beginning in 1983 with Freeport Exploration followed by Sunshine Mining, Crown Resources, New Concepts Mining, Royal Gold and most recently, Royal Standard Minerals ("RSM").
Drilling by previous operators totals 89 surface holes and 30 underground core holes for a total of 16,994 meters. RSM undertook underground development, exploration and bulk sampling of the deposit over several campaigns from 2004 to 2012, and constructed a 400 ton per day mill facility with a gravity recovery system. Gold mineralization is outlined over a strike length of 335 meters and to a vertical depth of over 150 meters, and is open along strike, down-dip and down-plunge toward the northwest. Several resource estimates were prepared for the deposit from 1997 to 2011, none of which are NI 43-101 compliant. Scorpio Gold acquired the property from RSM in December 2012.
The Goldwedge deposit exhibits several styles of gold mineralization from fault breccia and vein hosted to stratabound replacement style in limestone and pervasive quart-sericite-pyrite alteration hosted.
Goldwedge Exploration Drilling
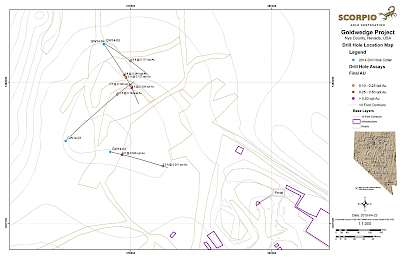
In 2014, Scorpio Gold drilled four oriented core holes from surface to gain further knowledge of the Goldwedge geology and controls to the mineralization. Significant results from the 2014 surface drilling are presented in the Company's April 27, 2015 news release.
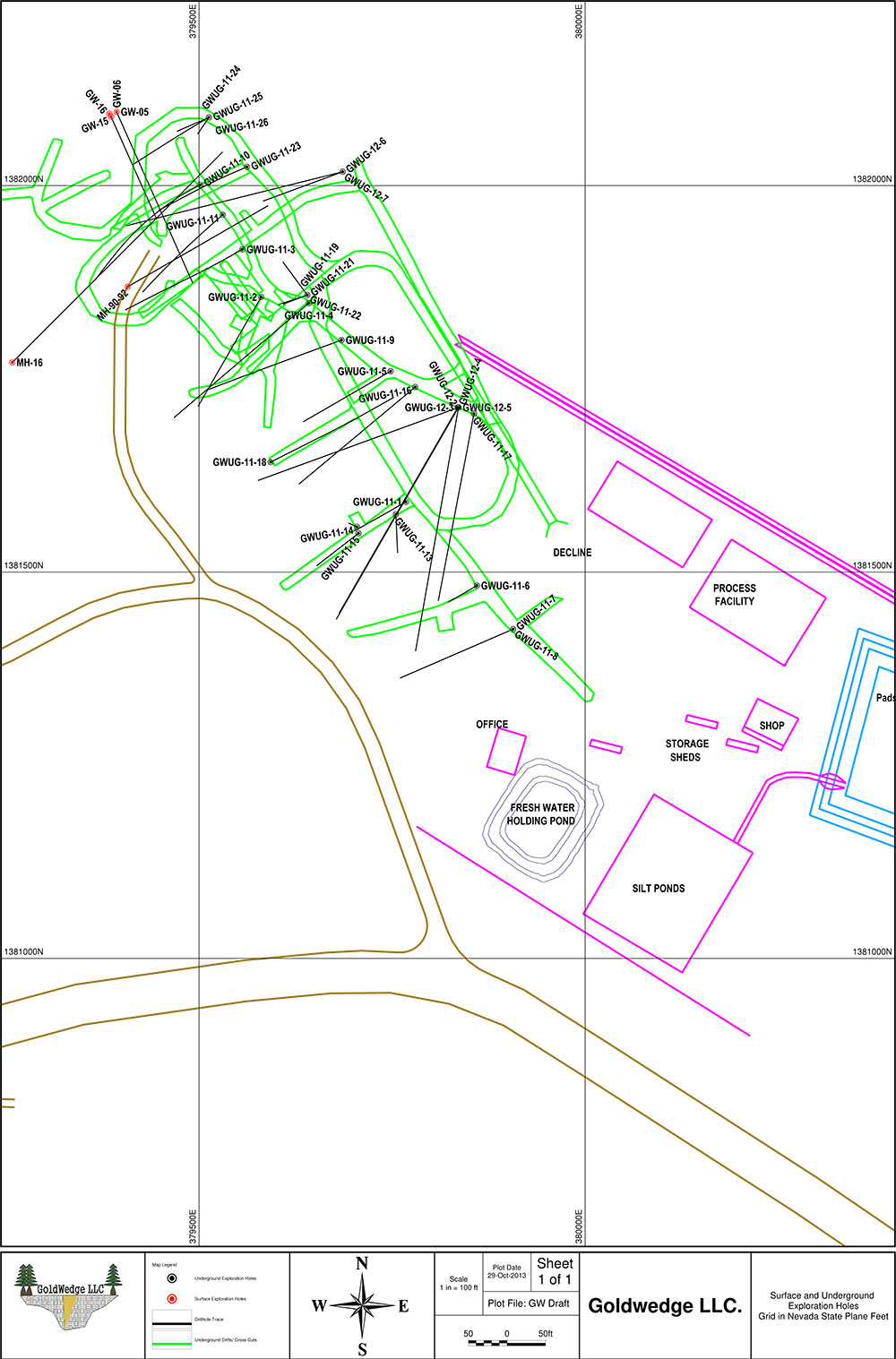
In 2015, the Company drilled 21 core holes from 6 underground drill stations totalling 4,695 ft (1,431 m). The majority of holes were drilled perpendicular to N60W trending Cambrian-Ordovician aged sedimentary host rocks. Results from the underground drilling indicate that mineralization at Goldwedge is related to the N30W trending Reliance Fault Zone, with mineralization occurring within and subparallel to the fault and as dilational lenses and veins extending outward from the fault zone along fractures oriented sub-parallel to bedding.
Mineralization of interest (0.03 OPT or 1.0 g/t and greater) was intersected in all 21 underground holes drilled in 2015. Results considered of significance for this deposit (0.10 OPT or 3.3 g/t and greater) were returned in 9 of the 21 holes (see September 8, 2015 news release). Several of the holes were drilled to verify historical drilling results; however, Scorpio Gold was unable to replicate the more substantial downhole widths and grades reported in 2011-12 drilling by the project's previous operator (as presented in the Company's November 4, 2013 news release).
Goldwedge 2015 Underground Drilling - Cross Sections
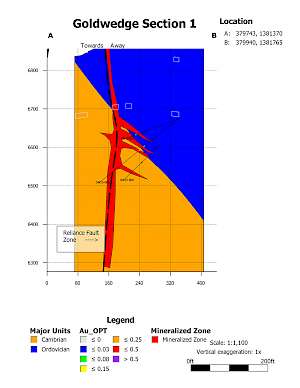 Goldwedge Section 1 |
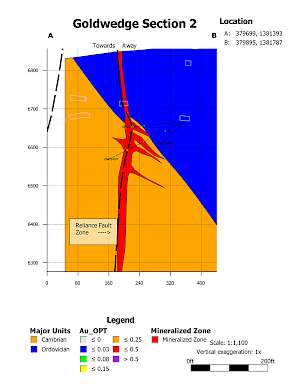 Goldwedge Section 2 |
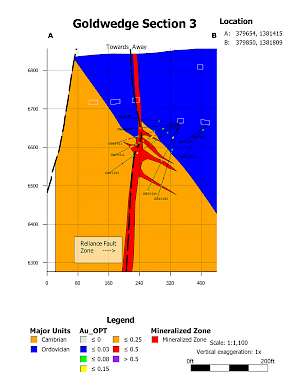 Goldwedge Section 3 |
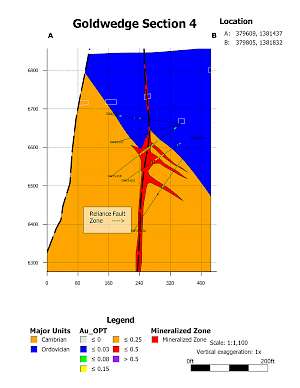 Goldwedge Section 4 |
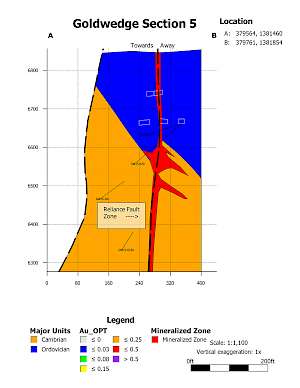 Goldwedge Section 5 |
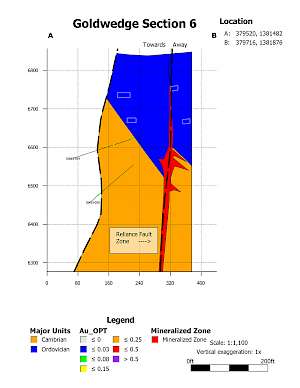 Goldwedge Section 6 |
2017 Surface RC Drilling
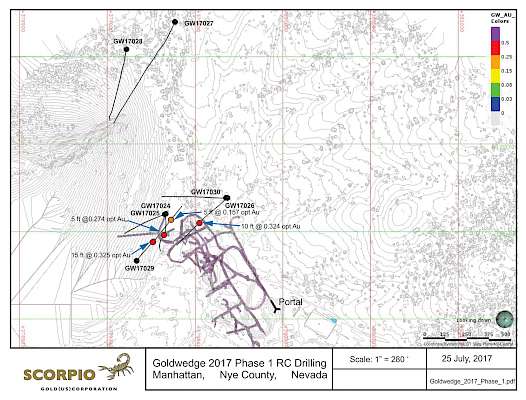
In 2017, Scorpio Gold drilled seven RC holes from surface to target the extension of the favorable lithologic unit in the Goldwedge Mine, specifically the Zanzibar limestone bound within the Reliance Fault Zone. This zone plunges northward into the Manhattan caldera margin. Seven RC holes totaling 7,530 ft (2,295 m) were drilled from 5 pad locations.
Significant mineralization was encountered in 3 of the holes (GW17024, GW17026 and GW17029) that intercepted the targeted Zanzibar limestone within the Reliance Fault Zone. GW17029 targeted an area near elevated underground rib samples west of the Reliance Fault Zone, and intersected significant mineralization (11.14 g/t gold over 4.57 m) within 65 feet of the mineralized rib and above the lowest working underground level (July 27, 2017 news release).
 2017 Surface Drilling Plan |
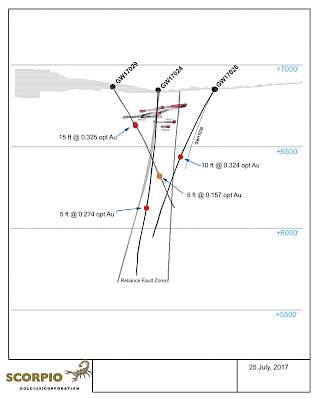 2017 Surface Drilling Cross Section |
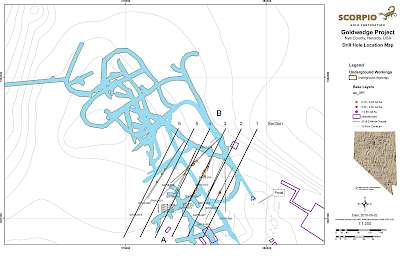
2020 Underground Drilling
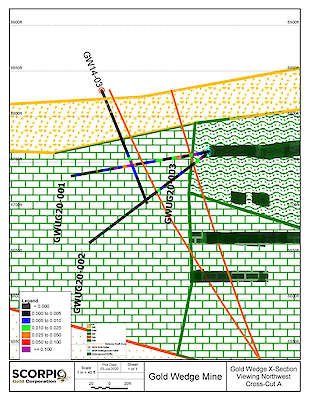
The 2020 underground drilling program focused on resource definition in areas where the Company’s 2014 surface drilling intersected higher-grade mineralization proximal to existing underground workings. As presented in the Company's July 27, 2020 news release, the first 3 holes intersected several mineralized zones, the most significant being a 7.6 meter intersection averaging 12.47 g/t gold and 176.23 g/t silver, which included 1.52 meters grading 53.49 g/t gold and 0.15 meters grading 3,960 g/t silver. The mineralized zones lie approximately 30 meters (100 ft) below surface and extend immediately southeast from existing underground workings. Additional results are pending.
Historically, silver has not been the primary target in the Manhattan mining district. Based on the high-grade silver intersections encountered in these holes however, a review of core samples and logs from previous drilling will be undertaken for evidence of other significant silver mineralization.
Keystone-Jumbo Project Area
The Keystone-Jumbo project area is located ~4 km southeast of the Goldwedge deposit and mill, and along strike of the regionally significant N30W trending Reliance fault zone, which trends through Goldwedge and the Manhattan Mine East and West pits. Geologically, the Keystone and Jumbo deposits occur near the northern margin of a Cretaceous granite intrusion within limestones, argillites, quartzites and schists of the Cambrian Gold Hill Formation. Mineralization is controlled by high-angle N30W faults transected by a weaker N30E and N80E structural fabric. Intersections of these fabrics control the high-grade gold mineralization in the historic Keystone and Jumbo pits.
The gold itself is localized within fault breccias and silicified metasediments in the Keystone and Jumbo pits as well as oxidized quartz-pyrite-gold veinlet stockworks in the clay alteration halos surrounding the core of the known mineralization. Hydrothermal alteration/mineralization affects the Mesozoic granites and some low-volume younger volcanics, suggesting that the age of the gold bearing system is mid to lateTertiary and may be genetically related to the Round Mountain-Toquima caldera complex.
Limited historic surface drilling at Keystone reported substantial downhole widths and grades, leading Nevada Goldfields to undertake a small open pit excavation in 1990 that recovered 5,750 ounces of gold. A preliminary review of the available data indicates that significant drill intercepts lie below and to the southeast of the open pit. A small open pit was also excavated around the same time on the Jumbo deposit. New Concept Mining reported mineral resource estimates for both the Jumbo and Keystone deposits in May 1997; however, neither estimate is compliant with NI 43-101 and await verification.
2019 Exploration Drilling Program
Scorpio Gold conducted a first-phase exploration diamond drilling program in the Keystone-Jumbo area in mid 2019. Nine exploration holes totalling 628 meters were drilled to test an area of previously reported surface soil sampling anomalies as well as structures relating to historic mineralization within the Keystone-Jumbo claim block (see 2016 program below and December 15, 2016 news release). Drill hole KP19-DDH-01 was collared within the Keystone pit to test the intersection of two high-angle NW and NE trending faults. The hole intersected mineralized polymictic breccia for its entire 19.2 meter length and returned 2.18 g/t Au over 14.63 m (December 6, 2019 news release). Visible gold was noted in silicified breccia and fractured quartzite within hole KP19-DDH-03 (photo); however, assay results were negative for gold in the samples taken. Results of the drilling have provided valuable new information on the controls to mineralization in the area and a second phase of drilling is planned.
2016 Exploration Program
Scorpio Gold completed a soil sampling program and ground magnetic/VLF electromagnetic survey over the Keystone-Jumbo project area in mid-2016. The geophysical survey was designed to assist in structural interpretation of the area and the soil sampling program to detect anomalous gold mineralization in areas covered by overburden. In the Keystone-Jumbo area, overburden covers approximately 85% of the land position and typically ranges from 0 to 2 meters depth.
Results outlined a 1,230 meter long soil anomaly that crosses nearly the entire NW length of the Keystone Jumbo land holdings. The anomaly follows a distinct N30-45W trending structural break that is sub-parallel to the N30W structure mapped in the Keystone pit, which is determined to be the main structural control to mineralization (see November 14, 2016 and December 15, 2016 news releases).
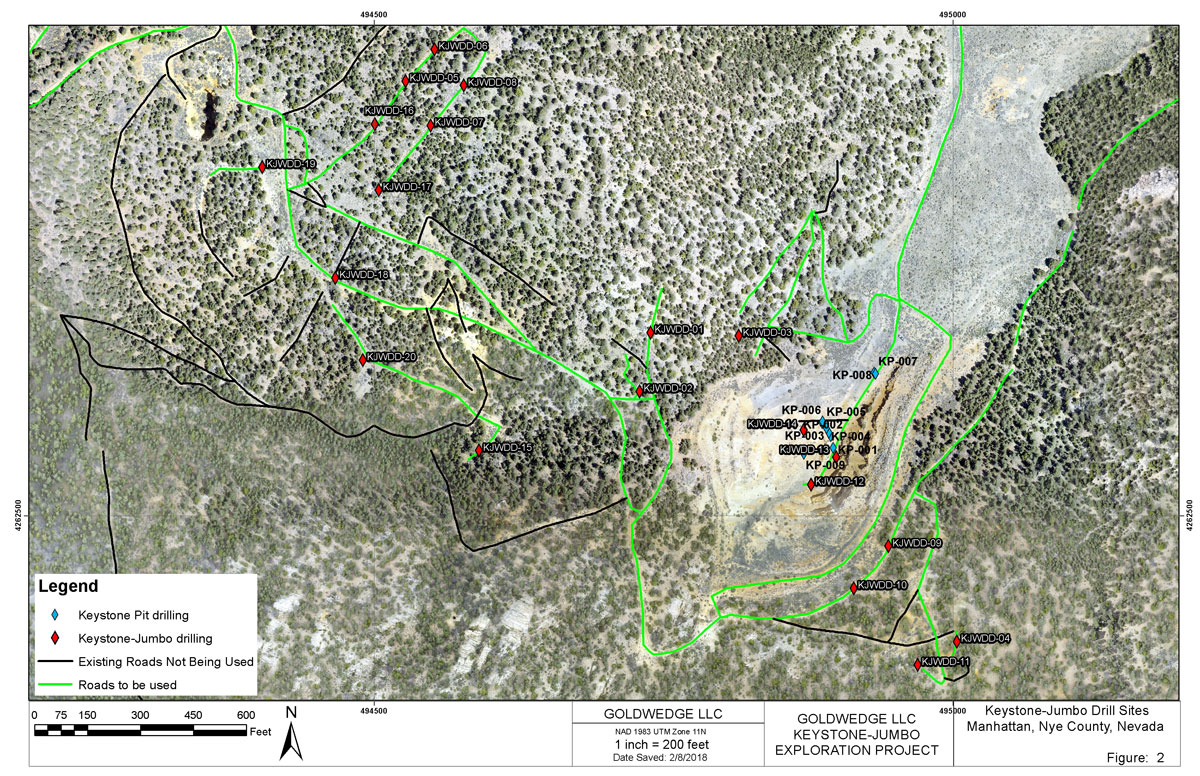
Keystone-Jumbo Permitted Drill Sites
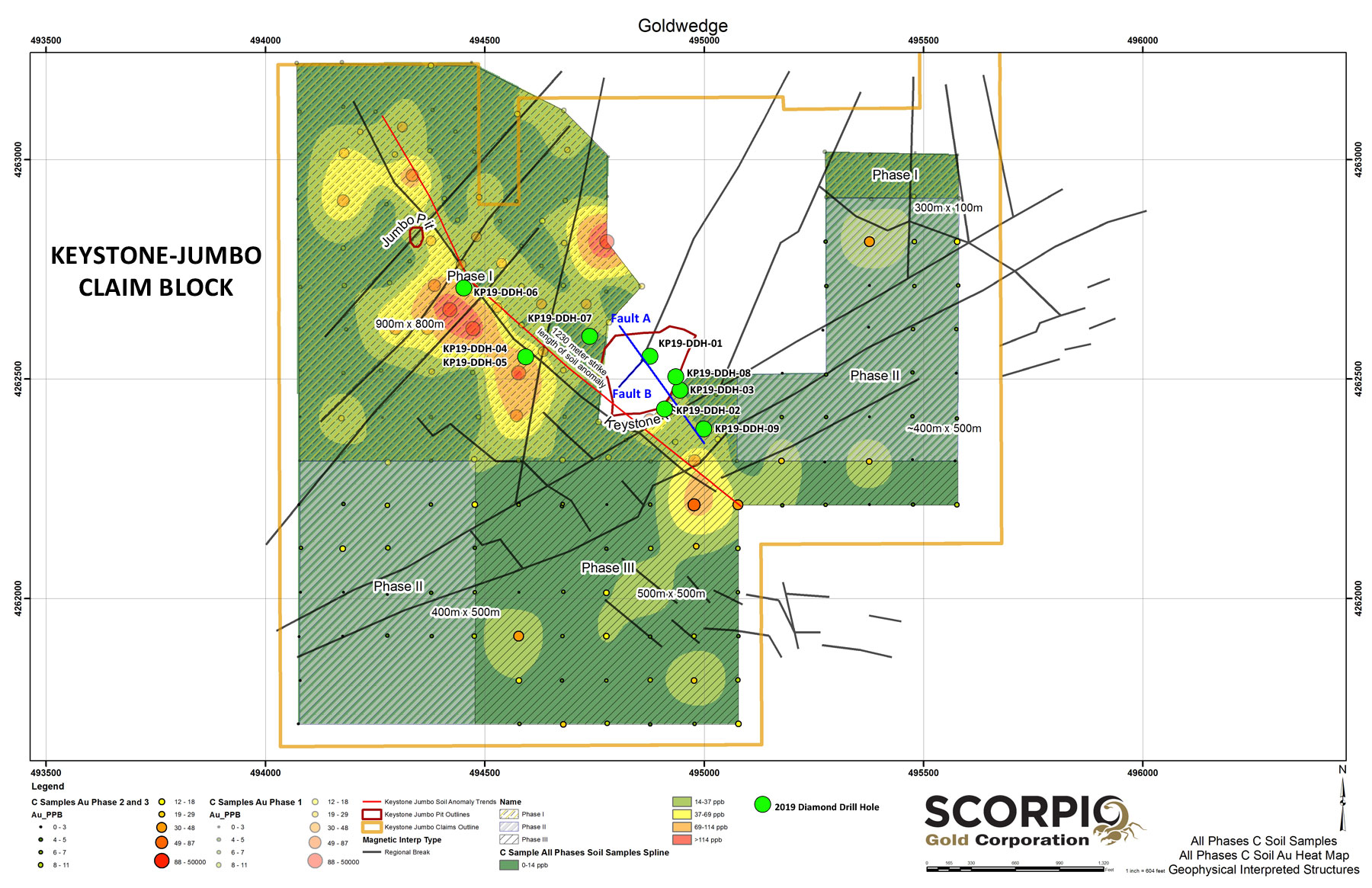
2019 Phase 1 Drill Hole Locations